Do You Know Why EN81-20 Updated the New Standard?
Cause there are many accidents for cabin cutting people and pit accidents, unfortunately, many elevator suppliers do not give this if they do not understand EN81-20 completely.
These updates are based on the initial standards developed in 2014, reflecting ongoing improvements and adjustments based on industry feedback and technological advances.
What Standards are Updated in the Latest EN 81-20?
1. UCMP Passenger Safety Enhanced
The Unintended Car Movement Protection (UCMP) system is designed to prevent accidental elevator movement. When the elevator is at the designated floor level and the doors are open, the UCMP safety device will immediately activate if the elevator starts to move unexpectedly, stopping the elevator instantly.
Dazen ensures that every elevator is equipped with a UCMP system before it leaves the factory, providing an added layer of safety for passengers.
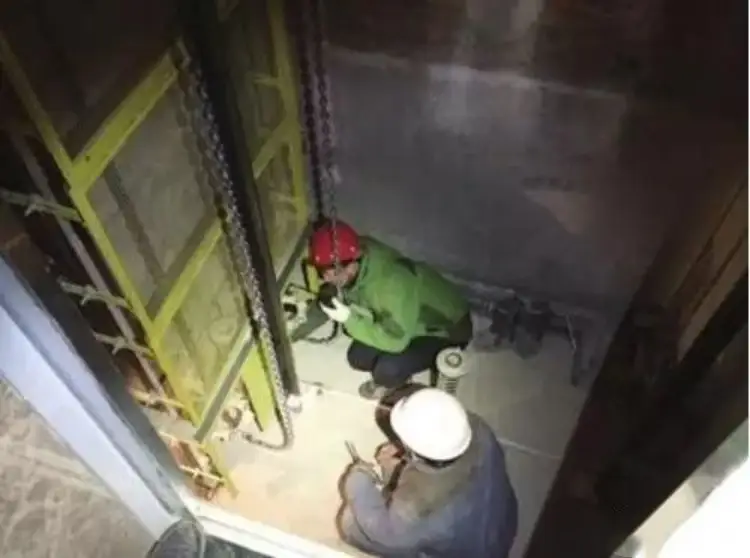
2. Safety Measures for Elevator Technicians
Since multiple technicians may be operating on the car roof and in the pit, each person must ensure their own protective space. Consequently, the required shelter space on the car roof and in the pit has increased compared to the previous version of the elevator standard. Additionally, signs on the car roof and in the pit must now indicate the maximum number of people allowed to enter these spaces.

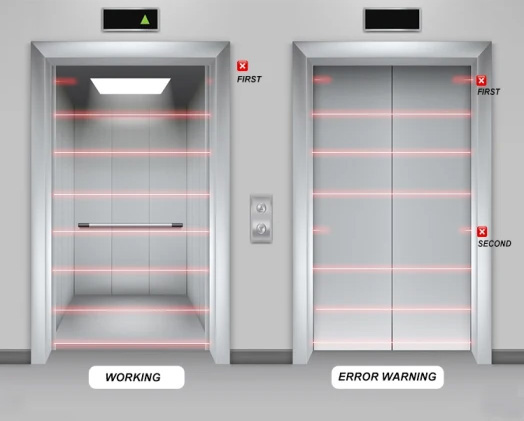
3. Elevator Door Detector
To reduce the risk of elevator doors hitting passengers as they enter and exit, the new standard enhances the range, resolution, and failure protection of door safety systems. Resolution refers to the blind spot in light curtain detection. The new standard mandates that throughout the entire door-closing process, the resolution of the door protection system must be at least 50mm. This means any obstruction larger than 50mm will be detected, prompting the door to reopen and preventing injury. The introduction of this new European standard will eliminate non-compliant products from the market, promoting a virtuous cycle of improved safety and quality.

4. Fire Protection Classification of Elevator Car Materials
The supporting structure of the car should be made of non-combustible materials.
The choice of finishing materials for the car floor, car walls, car doors and car ceiling should comply with the following fire protection requirements of EN 13501-1:
Floor: C-s2
Car walls and car doors: C-s2, dl
Car ceiling: C-s2, d0
(C refers to the “reaction to fire” classification, s and d refer to the classification of the material for the formation of smoke and burning droplets/particles)

5. Elevator Car Roof Balustrades
The function of the balustrade on the car roof is to prevent maintenance personnel from accidentally falling into the shaft. The new standard stipulates that balustrades must be installed on the car roof if the free distance from the outer edge of the car in the horizontal direction exceeds 300mm. The standard also provides detailed guidelines for the installation size and location of the balustrades and requires that the balustrades have a warning symbol or notice indicating the danger of leaning on it. If the distance between the inner edge of the handrail and the elevator shaft wall is 500mm, the minimum height of the handrail must be 700mm. If the distance exceeds 500mm, the minimum height of the handrail must be 1100mm.

6. Elevator Car Door Locking Mechanism
Another major change in EN 81-20 is the addition of a “short-circuit operation” function to the car door locks and landing door locks. Most elevator failures are caused by door lock failures. In order to find the cause of these failures, practitioners need to short-circuit some door lock contacts. Practitioners may forget to remove the short-circuit device afterward, which will lead to the risk of the door contacts being short-circuited while the elevator is operating normally, which is a huge safety hazard. The “short-circuit operation” function can effectively avoid this hazard.
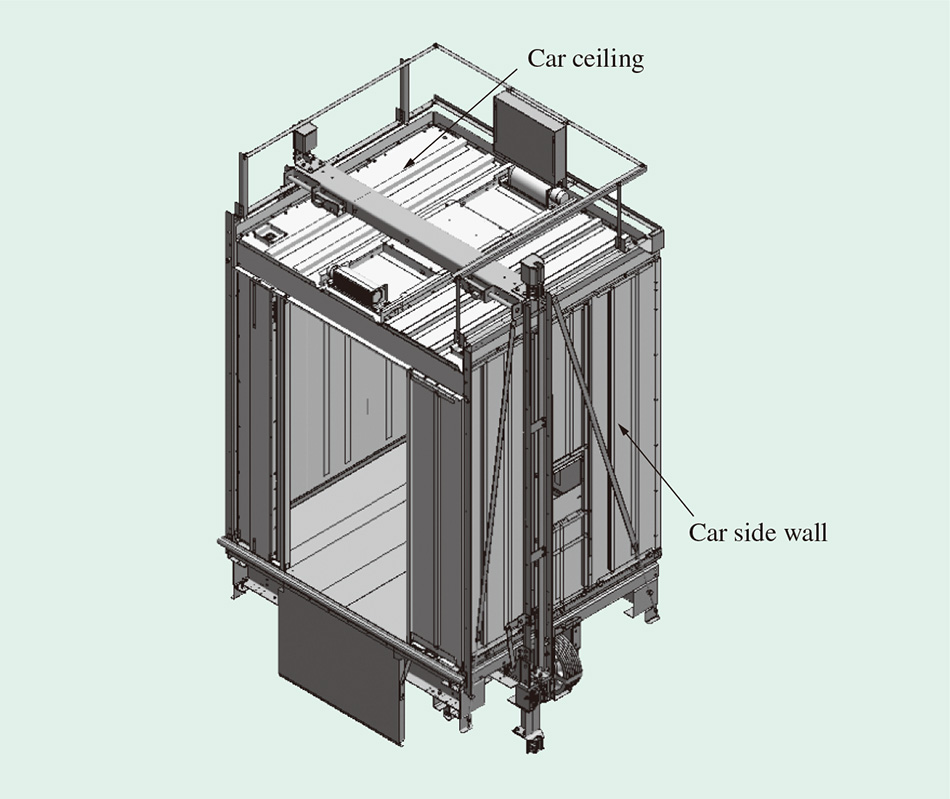
7. Car, Landing Door and Wall Strength
The new standard stipulates that the car walls, car floors, and car roofs must have sufficient mechanical strength. Additionally, the assembly of the car frame, guide shoes, car walls, car floors, and car roofs must possess enough mechanical strength to withstand the forces encountered during normal elevator operation, the action of the safety clamp, or the impact of the car on the buffer.
8. Elevator Car and Shaft Lighting
The car should be equipped with permanent electrical lighting devices to ensure that the illumination on the control device and at any point 1.0m above the car floor and at least 1.0m from the car wall is not less than 100 lux.
The shaft should be equipped with permanently installed electrical lighting devices. Even when all doors are closed, the car must achieve the following illumination requirements at any position throughout the journey in the shaft: a) The illumination at 1.0m above the car top within the vertical projection range of the car top must be at least 50 lux; b) The illumination at 1.0m above the ground must be at least 50 lux at any place on the pit floor where personnel can stand, work, and/or move between work areas.
To meet this requirement, a sufficient number of lights should be installed in the shaft, and additional lights can be installed on the car top as part of the shaft lighting system if necessary. Lighting devices should be protected from mechanical damage.

9. Access Doors, Safety Doors, Access Trap Doors and Inspection doors Dimensions
To ensure safe and convenient access for technicians, these doors should meet the following dimensions:
a) The height of the access door to the machine room and shaft should be no less than 2.00m, and the width should be no less than 0.60m;
b) The height of the access door to the pulley room should be no less than 1.40m, and the width should be no less than 0.60m;
c) The net size of the access trap door for personnel to enter and exit the machine room and pulley room should be no less than 0.80m×0.80m, and it should be able to remain in the open position after opening;
d) The height of the safety door should be no less than 1.80m, and the width should be no less than 0.50m;
e) The height of the inspection door should not exceed 0.50m, the width should not exceed 0.50m, and it should be of sufficient size to carry out the required work through the door.

The above list highlights the main refinement criteria of EN 81-20. There are, of course, many more details. If you want to learn more about the refinement criteria, you can consult Dazen’s sales team. We will be happy to provide you with detailed answers.
