What is an Escalator?
An escalator is like a moving staircase that helps people go up or down between different floors in buildings. It’s powered by electricity and has steps that keep going in a loop, allowing passengers to step on and off as needed. One of the cool things about escalators is that they can carry people non-stop, making them more efficient than elevators in terms of passenger capacity.
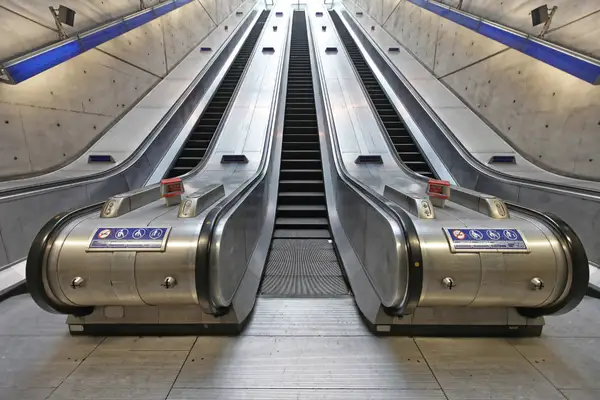

Escalator Working Principle
An escalator comprises two sets of conveyor belts: a chain conveyor belt and a friction conveyor belt. The chain conveyor belt consists of a series of rungs that are dragged by a rung conveyor chain. On the other hand, the friction conveyor belt is a handrail belt made of conveyor tape.
Both conveyor belts are driven by the same “drive spindle,” and their linear speeds are synchronized by adjusting the transmission ratio between the handrail shaft and the drive spindle.
The transmission between the main unit and the driving spindle occurs through a chain drive. The motor’s output power passes through a reduction gearbox to control the spindle’s speed via the host sprocket and the driving sprocket’s transmission ratio. Then, the step sprocket regulates the linear speed of the pedal conveyor chain.
The handrail belt drive sprocket on the drive spindle drives the handrail belt friction wheel. Through the friction between the friction wheel and the handrail belt, the handrail belt runs at a speed synchronized with the steps’ movement.
Escalator Structure
1. Driving Device
The drive unit is to provide the power to run the steps and handrail belt, commonly used end drive, the structure includes an electric motor, reducer, brake, transmission chain, and drive spindle.
a) Electric Motors
Typically, deep slot or double squirrel cage asynchronous motors are employed, as they possess substantial starting torque.
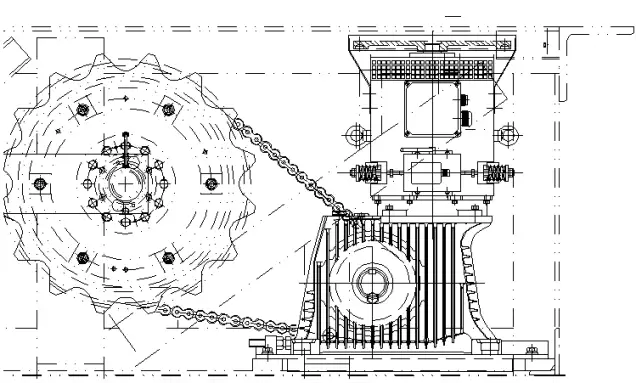
b) Working Brake
The brake is installed on the high-speed shaft of the speed reducer to provide braking power when the escalator stops running.
There are two types of brakes: belt brakes and block brakes.
c) Reducer
Most of them adopt worm gear reducers with compact structure and smooth operation.
d) Transmission
Non-friction transmission: multi-row chain, double-row chain drive
Gear transmission
Friction transmission: triangle belt transmission
The most common is double-row chain drive
e) Drive Spindle
It is the hub of the drive, on the shaft is equipped with a pair of step drive sprockets, transmission sprockets and handrail belt drive wheels, in the step drive sprocket is equipped with an emergency brake.
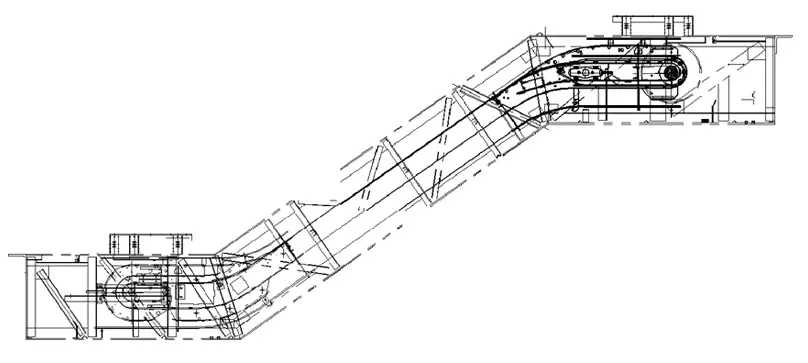
2. Stairway
The ladder road is the conveyor line of escalator, which mainly includes: step, step chain, guide rail, upper and lower steering wall.
The ladder way is divided into upper guide rail assembly, middle linear guide rail and lower guide rail assembly.
a) Steps
Escalators primarily rely on the rungs as their main load-bearing components, which come in two types: integral and split. These rungs consist of the tread, kick plate, bracket, main wheels, and auxiliary wheels.
The width of the rungs typically ranges from 580 to 1100mm, and their height does not exceed 240mm.

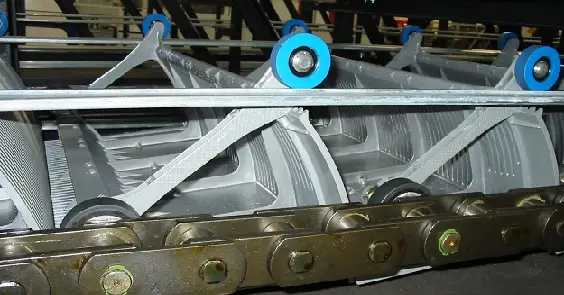
b) Conveyor Chain
The conveyor chain is a crucial component responsible for driving the escalator, usually in the form of a sleeve roller chain. It is imperative for the conveyor chain to possess sufficient strength, with a safety factor of no less than 5. Additionally, the conveyor chain must exhibit precise dimensional accuracy, ensuring that the deviation in length between two chains in the same section does not exceed 0.04%.

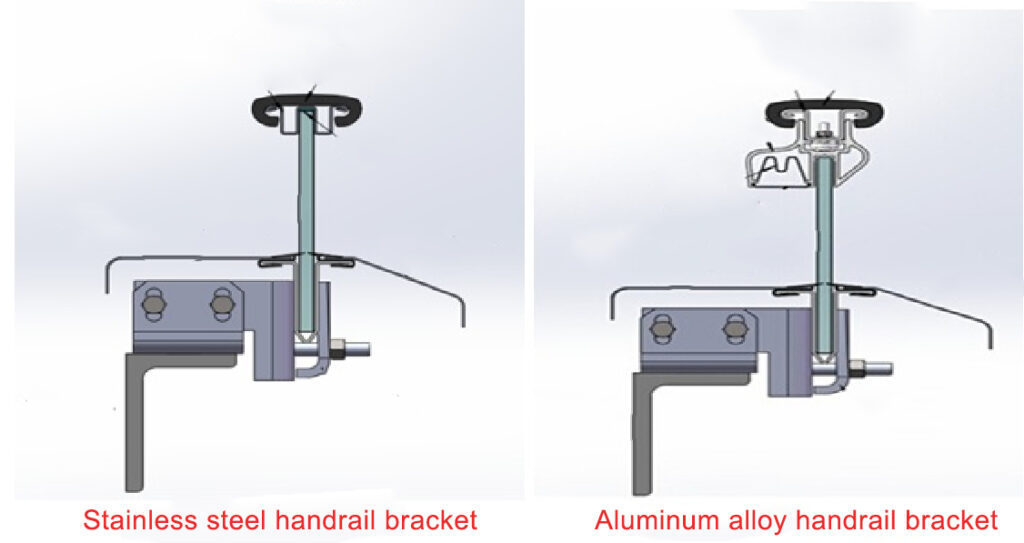
3. Handrail Device
The handrail device consists of various components, including the handrail belt, belt breakage protection device, apron plate, inner and outer cover plates, outer decorative plate, and finger protection device.
The purpose of the handrail device is to serve as a guardrail for passengers while they stand on the escalator, ensuring that the speed of their upper body matches the speed of the escalator’s movement.
The handrail operates using friction drive, with the pressure belt parts driven by the friction wheel.
The height of the handrail (measured from the step surface) must be within the range of 900mm to 1100mm.
For the glass wall plate, tempered glass with a minimum thickness of 6mm is utilized, and the gap between glass panels should not exceed 4mm.
The synchronization deviation between the running speed of the handrail and the step speed should be between 0% to +2%.
To ensure safety, the breaking load of the handrail should be at least 25KN. Alternatively, if this requirement is not met, a belt-breaking stopping device must be installed.
The apron plate, inner and outer cover plates, and outer decorative plate primarily serve decorative purposes.
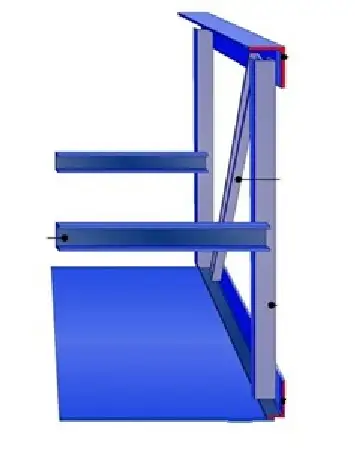
4. Truss
The truss, also known as the supporting member, is the skeleton of the escalator, which is used to carry the weight of the escalator components and the weight of the passengers. Its structure is basically the same as the escalator support structure. Usually, for public transportation escalators, there are several intermediate supports in the inclined section to ensure that the deflection meets the standard requirements.
The escalator truss structure is usually made of angle steel or square tube.
The truss, also referred to as the supporting member, serves as the backbone of the escalator, bearing the weight of the escalator components and passengers. Its structure closely resembles that of the escalator support structure. In public transportation escalators, the inclined section typically includes several intermediate supports to ensure that the deflection meets the required standards.
The escalator truss structure is commonly constructed using angle steel or square tubes. These materials provide the necessary strength and rigidity to support the escalator’s load and ensure its safe operation.
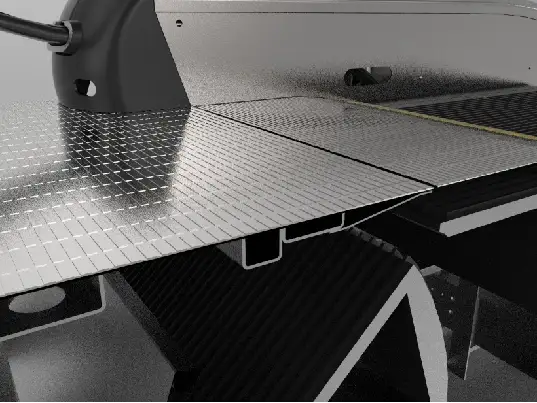
5. Cover Plate Assembly
The cover plate assembly is mounted on a portion of the horizontal section at the upper and lower ends of the escalator truss and serves as a connecting passageway for passengers entering or exiting from a stationary building to the escalator treads that continuously convey passengers. The comb teeth are mounted on a comb support plate for engaging movement with the treads.
6. Lubrication System
The lubrication system consists of oil pumps, oil pots, oil tubes and nozzles, etc. It serves to lubricate the transmission parts such as the main drive chain, the pedal link, the armrest drive chain and so on.
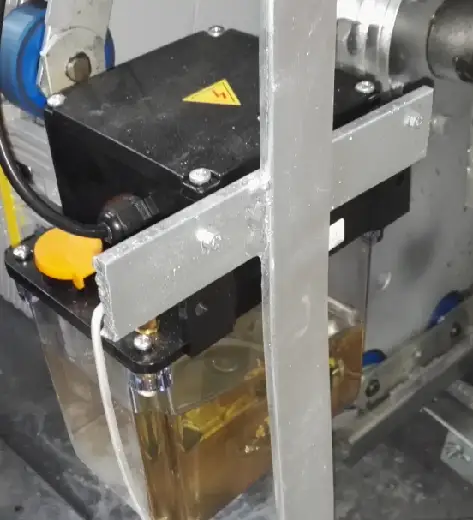

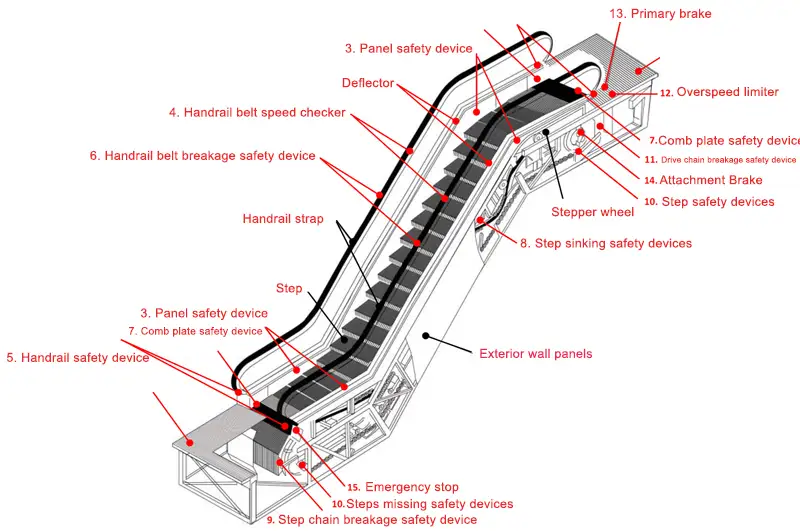
7. Safety Devices
The escalator is equipped with a host drive chain protection device. When the host drive chain breaks or elongates, the drive chain breakage protection device will act, and the touch protection switch will act to cut off the power supply of the safety circuit, and the escalator will stop running.
Escalator Main Parameters
1. Vertical Rise (Rise height)
Small height – less than 6 meters
Medium height – 6 ~ 20 meters
Large height – greater than 20 meters
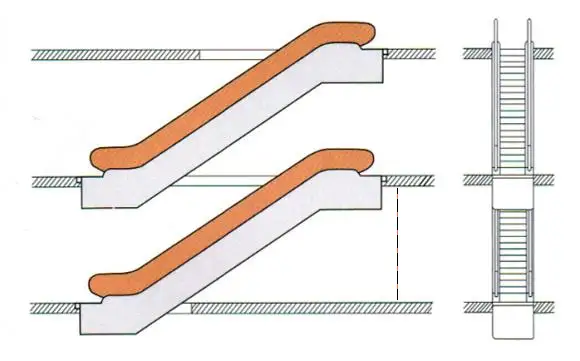
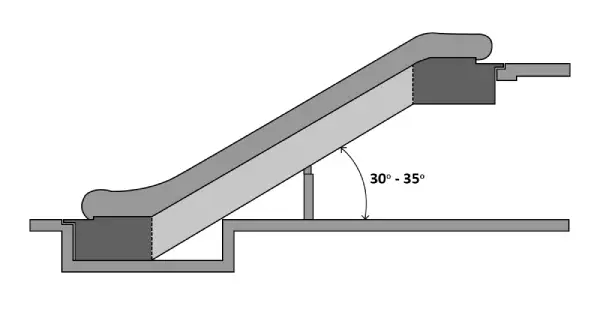
2. Inclination Angle
The standard angles for escalators are 35°, 30°, 27.3°, and 23.2°.
When the height ≤ 6m, V≤0.5m/s , the inclination angle ≤ 35°.
3. Running Speed
When the inclination angle>30°, the speed V≤0.5m/s
When the inclination angle ≤30°, the speed V≤0.75m/s
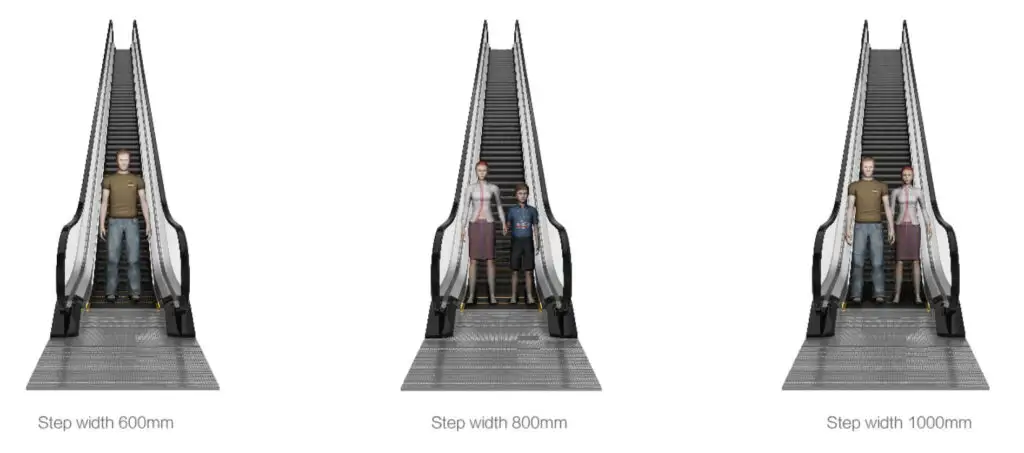
4. Step Width
The standard step width: 600mm, 800mm, 1000mm.
Actual step width:
Width: 580 ~ 1100mm
Depth: ≥ 380mm
Height: ≤240mm

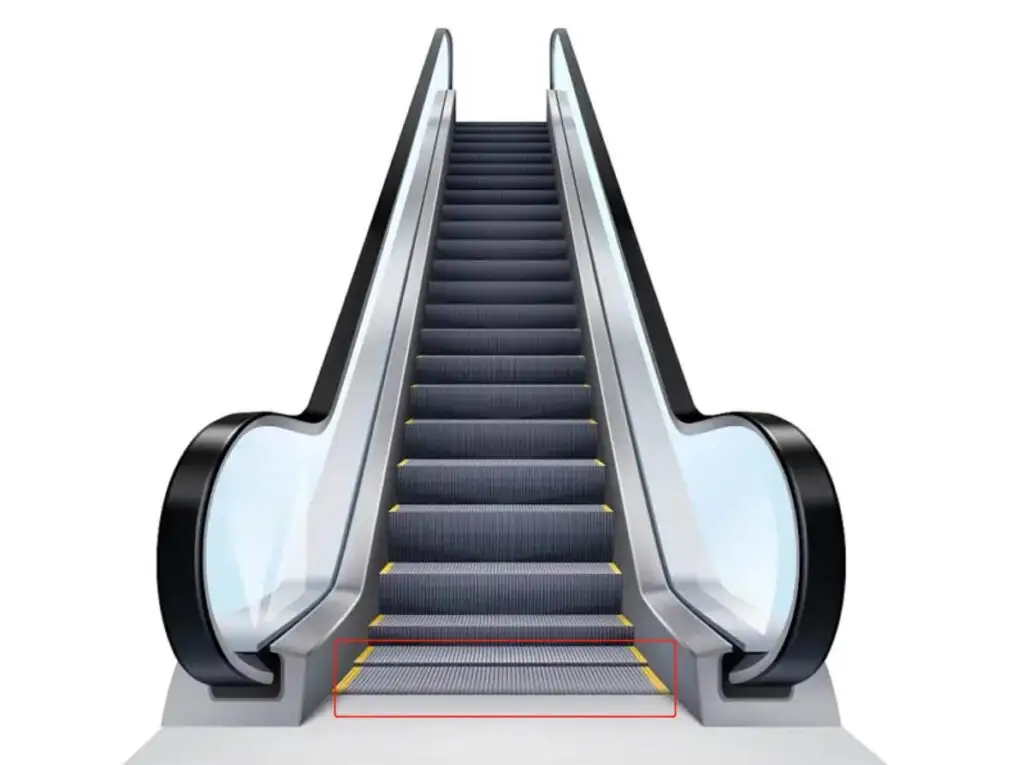
5. Horizontal Steps
K type n=2 for H≤6m V≤0.5m/s
M type n=3 for H>6m or 0.5m/S< V≤0.65m/s L-type n=4 for H>6m and V>0.65m/s.
The national standard requires that the length of the horizontal section should not be less than 800 (i.e. at least 2 steps).

6. Radius of Curvature
Speed V ≤ 0.5m / s: the upper R≥1.0m, the lower R≥1.0m
Speed 0.5<V≤0.65m/s: the upper R≥1.5m, the lower R≥1.0m
Speed 0.65<V≤0.75m/s: the upper R≥2.6m, lower R≥2.0m
Escalator Running Speed Calculation
For example:
Motor rated speed: w = 960r/min
Reduction ratio of reduction gearbox: I=24.5
Number of teeth of host sprocket: z1=23
Number of teeth of driving sprocket: z2=65
Pitch diameter of step sprocket: D=0.6834m
Number of teeth of folio sprocket: z3=30
Number of teeth of handrail sprocket: z4=26
Diameter of friction wheel: D1=0.587m
Thickness of handrail belt: t=0.01m
It can be calculated from above:
Spindle speed w0=w/Iz1/z2=960/24.523/65=13.8650r/min=0.231r/s
Linear speed of step transfer chain v=w0Dπ=0.2310.68343.14=0.496m/s
Handrail shaft speed w1=w0z3/z4=0.23130/26=0.267r/s
Handrail belt linear speed v1=w1D1π=0.267(0.587+0.01)3.14=0.501m/s (calculated according to the center of the handrail belt)
If you are considering the installation of an escalator or in search of a reliable escalator supplier, look no further than Dazen. Our escalators have been successfully exported to 50 countries worldwide, and we take pride in our entire range of elevators and accessories that have obtained CE certification. Contact us today to receive a complimentary quote for your escalator needs.
